Molecular Docking in Reumatoid Arthritis studies for MVS Pharma
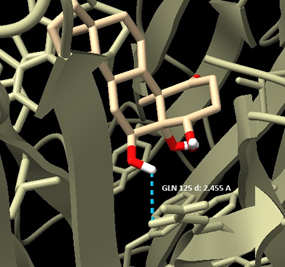
Bioactive Compounds against TNF-α in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a well known systemic inflammatory disease affecting people across diverse age groups and genders. RA usually affects the lining of the joints, leading to erosions of the cartilage and deformity of bones and joints. In some cases, joint inflammation can manifest generalized systemic symptoms as well as inflammatory involvement of non-articular organs. A well known receptor of RA, is tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) receptor, for which the over-expression has been shown and documented that it is involved in tissue damage and joint inflammation.
Over the years, different treatments have been proposed: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), methotrexate (MTX), anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs), natural actives such as GLA, GOPO, Phytosterols β-sitosterol, gallic acid, ascorbic acid, astragalin and tormentic acid, antioxidants (Vitamin C, vitamin E, carotenoids, polyphenols and antioxidant enzymes) and herbal formulations. However, side effects have been found associated with these medications. What are the alternative options that could be explored? To reduce the side effects, the scientific community shifted its attention towards new active compounds derived from natural plant extracts, such as rose hip, as potential candidates for novel RA treatments.
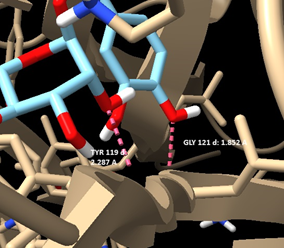
Building upon the interest in bioactive compounds for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), at SinodosChemistry.com we use computational tools such as UCSF Chimera, AutoDock and others, as a valuable approach to screen different natural ligands against the TNF-α receptor. This method minimizes the time required for screening and provide a cost-effective alternative to the experimental procedure.
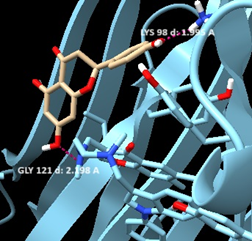
Our research for MVS Pharma, has shown that among the selected natural compounds: Staurosporine, Somnifericin and Withanolide L possess the highest binding affinities and the interactions present between the ligands and the receptor are consistent with the results from previous studies. The 3D X-ray crystal structure of TNF-α, was obtained from the Protein Data Bank under the PDB ID: 2AZ5 (https://www.rcsb.org/structure/2AZ5). Bioactive compounds were selected for their binding affinities sourced from previous studies and their presence in rose hips. Also, they were chosen based on the availability of their 3D structures in SDF format. The ligands were downloaded from PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/).
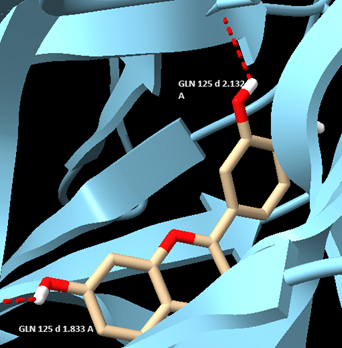
This outcome suggests the potential of these compounds as candidates for the development of RA treatments. Our capabilities enable us to contribute to this ongoing research and validate potential interactions of new bioactive compounds for RA therapeutic treatments. In a continuing process, we are screening tens of other bioactive compounds against the receptors used in the first work.
Contact us to discuss your needs in drug design, molecular docking simulations, pharmacokinetic studies and more!
