COVID -19 Drug research via Molecular Docking study
SARS- Cov -2 virus has caused the global pandemic throughout 2020 and 2021. The novel coronavirus has high mortality, and its newest variations seem to also exhibit a higher spread rate. Many efforts have focused on finding a vaccine or drug to end the pandemic. The most logical and faster option for scientists and organizations world wide was to work on drug re- purposing: look for a potential anti- viral drug/ vaccine among existing solutions for similar viruses. SARS- CoV-2 structure is known, and its proteins structures have been created via crystallography approaches and can be found in free databanks online [such as PubMed, Drug Bank, etc]. The high similarity to previously discovered viruses, has led to the screening of drugs and vaccines against those viruses.
Drug screening is a computational approach which used various approaches to determine whether a drug has potential against a virus. The most popular screening approach is the ‘Molecular Docking’; in this methodology, the structures of drug, and virus’ proteins are prepared and let to interact with each other based on physical and chemical interactions that can be:
- Electrostatic interactions
- Hydrogen bonds
- Dispersion forces
- London forces
- Other types of interactions
Molecular Docking is a powerful technique to investigate such large body interactions which would be impossible to handle via approaches based on Ab Initio or Density Functional Theory. Of course, Large Scale Molecular Dynamics can also be employed, requiring however access to cloud for the required computational power.
Our client/ partner brought together a team of specialists in order to investigate whether a known drug and its metal complexes with Fe, Cu, Ag, Ca, Al, and others would be potential efficient drugs against SARS- CoV-2. We worked together in the following approach:
- Four protein virus proteins have been chosen as potential targets for our drug: 6M71, 6VYB, 6Y2E and papain like protease
- The required preparations took place in Chimera environment
- The drug model and its metal complexes were built in HyperChem environment
- AutoDock Vina was used for the Molecular Docking of the ligand against the four virus proteins
- The binding energies were extracted are evaluated
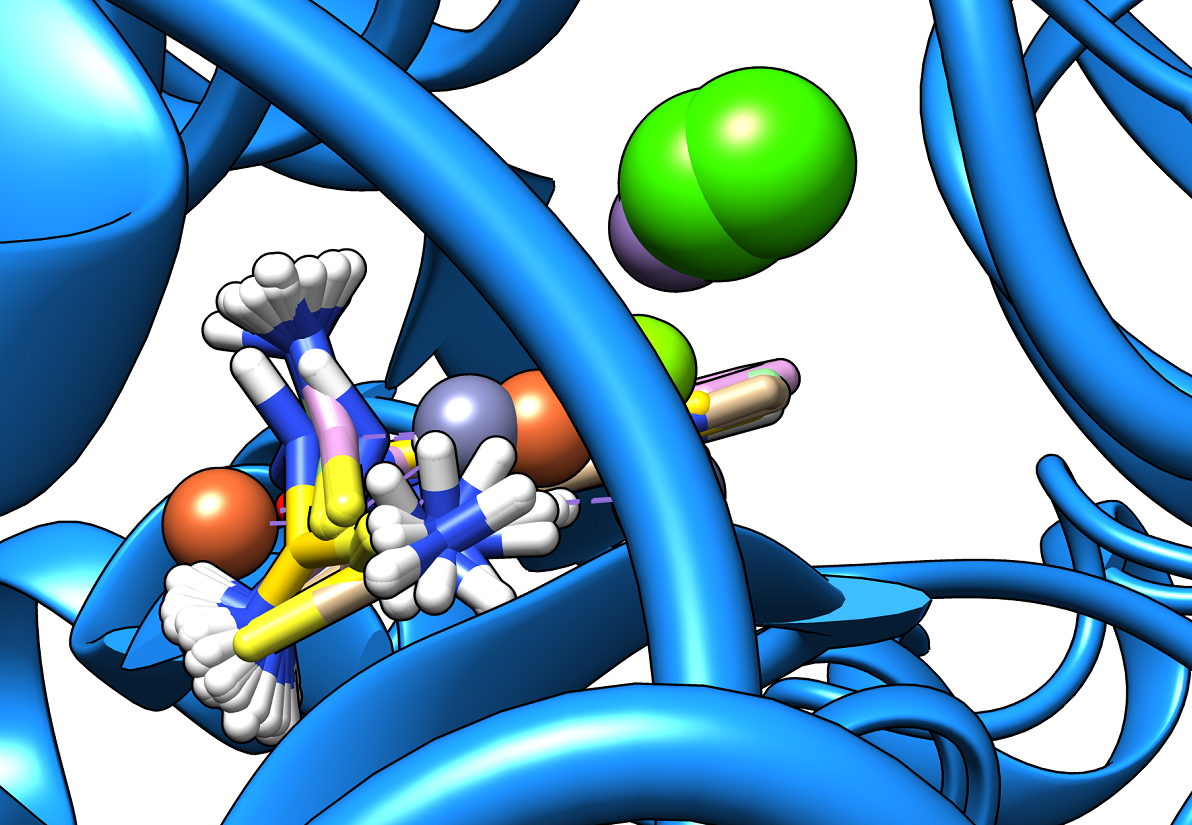
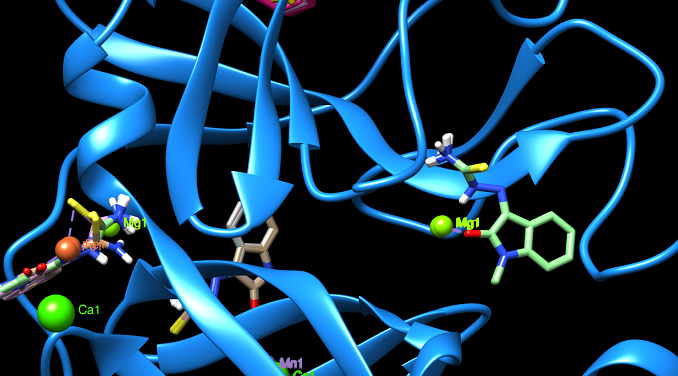
- The docking pockets in each protein were identified, depicted and investigated
We found that two specific metal complexes led to binding energies with at least two virus’ proteins higher than -8.0 kcal/ mol. These values confirm that the metal complexes of the initial drug are excellent candidates for ending the COVID-19 pandemic. Our findings are to be published [submission till January 30, 2021].
