Advanced Heat Exchangers: Design, Operation, Inspection and Troubleshooting
This advanced course covers all design and specification aspects of the different types of heat exchangers. Scientific principles, design principles, standards and industrial practices are presented to the attendants. Thermodynamics leading to design and operating specifications are covered in detail. Materials selection and manufacturing methodologies complete this 5-days seminar. Several optimization examples are included whereas the advantages and shortcomings of different HX are revealed. Novel approaches in manufacturing HX are also presented. Dimensionless numbers and similarity principle are explained in detail so that the attendant develops and understanding of designing HX for complex geometries and transient conditions.
Objectives:
By the end of the course, participants should have:
üAn overview of the related theory of heat [and mass] transport
üAn understanding of operating and maintenance of heat exchangers
üKnowledge of all heat exchangers types and classification
üKnowledge of control and monitoring approaches
üKnowledge of heat exchanger fluids
üKnowledge of sizing and design approaches
üKnowledge of case studies
üHands on calculations
Contents:
üTypes of heat exchangers
üScientific background
üThermodynamic principles
üApplications of heat exchangers
üClassification of heat exchangers
üDesign and sizing
üResistances to heat and mass transfer
üThermal conductivity, overall heat transfer coefficient
üCalculations and examples on heat transfer in various geometries
üCalculations and examples on heat transfer under steady state and transient conditions
üTypes of boundary and initial conditions
üNumerical and analytical solving of sets of differential heat exchange, velocity and momentum equations
üDimensionless numbers and dimensionless graphical approaches
üSimilarity principle
üCombined heat transfer [conduction, convection, radiation]
üCross flow, counter flow, and parallel flow comparison
üExamples and real time work on optimization of HX based on different type choices
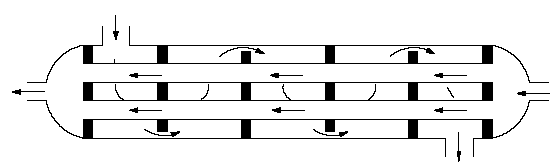
üShell and tube vs Plate HX
üSingle pass vs Multiple pass HX
üIonic Salts, Molten salts and other viscous heat transfer liquids
üCorrosion and erosion in HX
üInspection methodologies [Hydrogen, Hypersonic, pressurization, visual inspection]
üCompact and high compact HX
üNovel HX and novel manufacturing approaches; the atomic continuous approach
üCase studies
üRetrofitting
üControl and monitor
üOperational conditions
üFouling
üIntegration
üSimulation and modeling

Who should attend?
üMechanical Engineers, Chemical Engineers, Process engineers, workers, maintenance staff
üExecutives of oil and gas, chemical, manufacturing and petrochemical industries
üTechnicians and maintenance personnel
