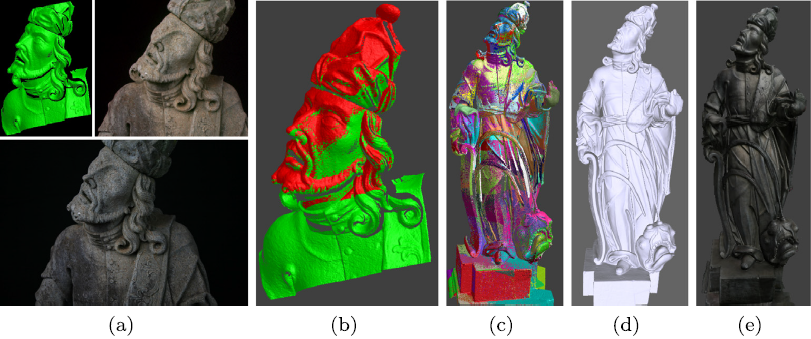
3D scanning Part C: Artefacts and art works related projects
Numerous works have been reported in the literature, revealing the potential of 3D scanning applications. Different ‘objects’ required different approaches and the most significant of them are presented in Table 1. Other, small scale works with novel approaches for 3D scanning are presented in a forthcoming article.